Edge detection
- Convert a 2D image into a set of curves
- Extracts salient features of the scene
- More compact than pixels
Origin of edges
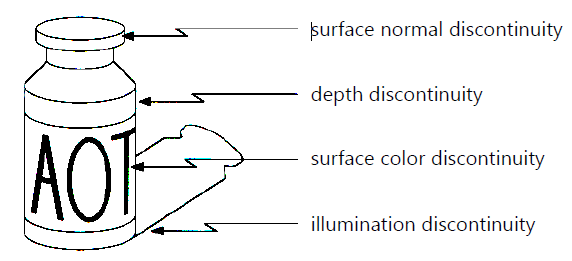
- Edges are caused by a variety of factors
Images as functions
- Edges look like steep cliffs
Characterizing edges
- An edge is a place of rapid change in the image intensity function
Image derivatives
- How can we differentiate a digital image $F[x,y]$
- Option 1: reconstruct a continuous image, $f$, then compute the derivative
- Option 2: take discrete derivative (finite difference)
$$\frac{\partial f}{\partial x} [x,y] \approx F[x+1, y] - F[x,y]$$
- How would you implement this as a linear filter?

Image gradient
- The gradient of an image: $$ \bigtriangledown f = [ \frac{\partial f}{\partial x} \frac{\partial f}{\partial y} ] $$
- The gradient points in the direction of most rapid increase in intensity
- The edge strength is given by the gradient magnitude:
$$||\bigtriangledown f|| = \sqrt{(\frac{\partial f}{\partial x})^2 (\frac{\partial f}{\partial y}})^2 $$
- The gradient direction is given by:
$$ \theta = tan^{-1} (\frac{\partial f}{\partial x} / \frac{\partial f}{\partial y}) $$
- How does this relate to the direction of the edge?

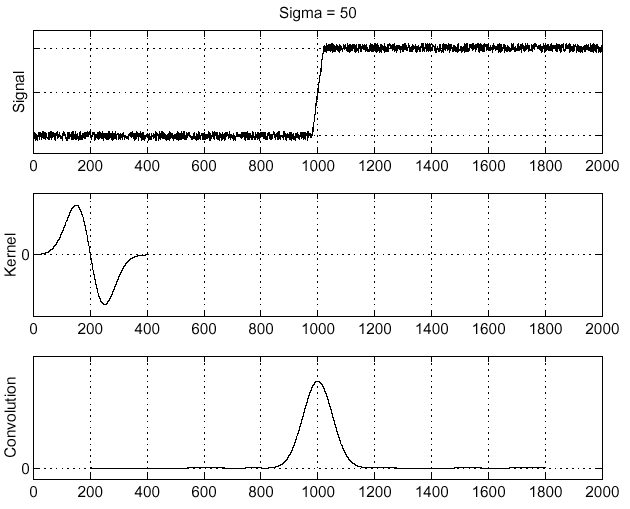
Effects of noise

- Where is the edge?
Solution: smooth first

To find edges, look for peaks in $ \frac{d}{dx} (f \star h)$
Associative property of convolution
Differentiation is convolution, and convolution is associative:
$$ \frac{d}{dx} (f \star h) = f \star \frac{d}{dx} h$$
This saves us one operation: $f$
The 1D Gaussian and its derivatives
$$G_{\sigma}(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi} \sigma} e ^ -({\frac{x^2}{2\sigma^2}})$$
$$G'_{\sigma}(x) = \frac{d}{dx} G_{\sigma}(x) = - \frac{1}{\sigma} (\frac{x}{\sigma}) G_{\sigma} (x) $$
2D edge detection filters

$$h_{\sigma}(u,v) = \frac{1}{2\pi \sigma^2} e ^ -({\frac{u^2+v^2}{2\sigma^2}})$$

$$\frac{\partial}{\partial x} h_{\sigma} (u,v)$$
Derivative of Gaussian filter

The sobel operator
- Common approximation of derivative of Gaussian

- The standard definition of the Sobel operator omits the 1/8 term
- doesn’t make a difference for edge detection
- the 1/8 term is needed to get the right gradient magnitude
Sobel operator: example


Example


- Which method is the best way to compute the derivative of an image?
Finding edges

Get Orientation at Each Pixel
- Get orientation (below, threshold at minimum gradient magnitude)

Non-maximum supression

- Check if pixel is local maximum along gradient direction
- requires interpolating pixels p and r
Before Non-max Suppression
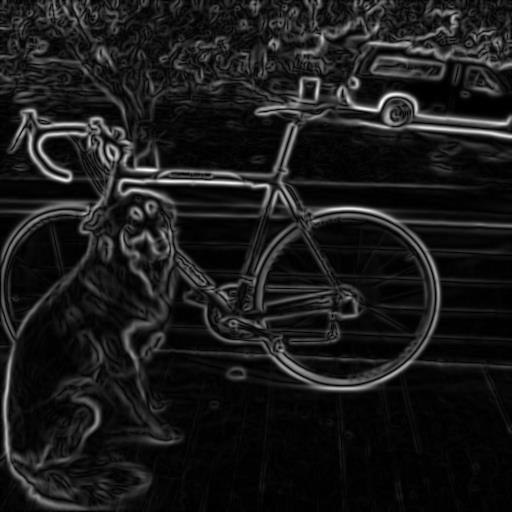

After Non-max Suppression

Thresholding edges
- Still some noise
- Only want strong edges
- 2 thresholds, 3 cases
- R > T: strong edge
- R < T but R > t: weak edge
- R < t: no edge
- Why two thresholds?

Connecting edges
- Strong edges are edges!
- Weak edges are edges if they connect to strong
- Look in some neighborhood (usually 8 closest)

Canny edge detector
- Filter image with derivative of Gaussian
- Find magnitude and orientation of gradient
- Non maximum suppression
- Linking and thresholding (hysteresis)
- Define two thresholds: low and high
- Use the high threshold to start edge curves and the low threshold to continue them
Reference: Lecture 1: Images and image filtering
'AI > Computer Vision' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Aliasing(엘리어싱) - 발생 이유, 결과, 방지 방법 (2) | 2022.06.01 |
|---|---|
| [CS5670] Lecture 4: Local features & Harris corner detection (0) | 2022.05.23 |
| [CS5670] Lecture 3: Image Resampling & Interpolation (0) | 2022.05.23 |
| [CS5670] Lecture 1: Images and image filtering (0) | 2022.05.19 |
| [CS5670] Lecture 0: Intro to Computer Vision (0) | 2022.05.19 |




댓글